Advertising Marketing Audiences in the Era of Consent Mode
In today’s digital age, user privacy has become a priority for both consumers and businesses. With the rise of regulations such as GDPR in Europe and CCPA in California, the way companies collect and use audience data has changed significantly. This post explores how Consent Mode is transforming the advertising landscape, allowing businesses to comply with privacy regulations while optimizing their campaigns and effectively segmenting their marketing audiences. Join us to discover the essential strategies and tools for navigating this new era of digital marketing.
Advertising Audiences
Advertising audiences are groups of people you want to target with your ads based on specific characteristics. These characteristics can include age, gender, interests, online behavior, or geographic location, among others. The goal of segmenting an audience is to show your ads to people who are more likely to be interested in your products or services, thereby increasing the effectiveness of your advertising campaigns.
Audiences in Digital Advertising
Digital advertising platforms use data collected from their users to allow advertisers to create and select these specific audiences. This makes digital advertising extremely personalized and targeted, and therefore often more effective than traditional mass advertising methods.
Imagine you have a sports equipment store. You might want to target your ads to people who have shown interest in sports, have recently visited sports websites, or even have purchased sports equipment online. By using the available information about these people, you can ensure your ads reach those who are most likely to become your customers, rather than wasting resources showing ads to people who probably aren’t interested in sports equipment at this time.
Identifying Your Potential Audience
Identifying the advertising audiences most aligned with your products or services is a crucial step in developing an effective marketing strategy.
To identify your potential audience, you need to find the key characteristics that define them as a group and differentiate them from other profiles. Analyze their age, gender, geographic location, interests, and/or behavior.
These actions can help you define and understand your target audience:
- Current Customer Analysis: Examine who your current customers are and why they buy your products or services. Look for common patterns in demographics, interests, and behaviors.
- Market Research: Conduct surveys, interviews, and focus groups to gather information about the needs, wants, and behaviors of your target market.
- Competitor Analysis: Observe who your competitors are targeting and how they communicate their messages. This can give you clues about market segments you might be overlooking.
- Buyer Persona Profiles: Create detailed profiles of your ideal customer based on prior market research and demographic data. Include information such as age, gender, education, income, challenges, and buying motivation.
- Social Media Analysis: Look at interactions, comments, and the most popular content.
- Keyword Analysis: Research what search terms people are using that might be interested in your products or services.
- Web Data Analysis: Examine the data from your website. See who your visitors are, how they reach your site, which pages they visit the most, and how much time they spend on your site.
- Market Trends and Industry Reports: Review industry reports and market studies to understand broader trends affecting your sector and how these might influence the needs and behaviors of your audience.
- Direct Customer Feedback: Don’t underestimate the value of direct feedback. Talk to your customers via emails, calls, or even in person to gain direct insights into their needs and experiences.
- Testing and Experimentation: Finally, don’t be afraid to experiment with different messages and offers to see what resonates most with different segments of your audience. Digital advertising campaigns, for example, allow you to conduct A/B tests to compare effectiveness among different audiences.
Defining and understanding your target audience is an ongoing process. As your business grows and the market changes, your audience may also evolve. Keep focusing on learning and adapting to ensure you are always meeting your customers’ needs as effectively as possible.
Online Tools to Define Audiences
Here are 10 tools that can help you collect, analyze, and interpret relevant data to precisely define your target audience. They include everything from market statistics and trends platforms to specific tools for conducting surveys and competitor analysis:
- ChatGPT: Uses advanced artificial intelligence to generate content ideas, answer questions, and provide real-time assistance, improving interaction and understanding of your audience’s needs. This year’s big novelty is ChatGPT.
- Clever Keyword Planner: With this keyword planner, you can research the keywords your potential audience uses in major search engines. It gets results for Google and Bing simultaneously.
- SEMrush: Provides keyword analysis and social media analysis of your competition. SEMrush helps you understand what your audience searches for in search engines, which content is most popular, and what is shared on social media, offering insights into your audience’s interests.
- Google Trends: Allows you to explore search trends on Google, helping you understand the interest in specific topics or keywords related to your business.
- Meta Insights: Offers data about your audience on Facebook and Instagram, including demographic information, interests, follower statistics, post performance, and more. The Meta Business Center is very interesting if you are present (which you should be) on social media.
- LinkedIn Analytics: Offers insights into who follows your company page, who interacts with your posts, and demographic details of your audience on LinkedIn. Explore LinkedIn Analytics on your professional LinkedIn profile.
- Clever Ads Manager: Provides reports and insights about your advertising campaigns and helps you analyze which audiences are most effective and profitable for your business. Clever Ads Manager is very interesting because it condenses all the information from your various advertising platforms into a single dashboard.
- Google Forms: an online survey tool that allows you to collect feedback directly from your target audience about their preferences, needs and behaviors. Try Google Forms now.
- Google Analytics: You’ve probably heard about Google Analytics at least once this year. This Google tool provides detailed information about your website visitors, including demographics, interests, behavior, and how they interact with your content.
- Microsoft Clarity: A Bing analysis tool that analyzes user behavior, providing heatmaps and session recordings to understand how users interact with your website, identifying areas for improvement to optimize the user experience.
1st Party, 2nd Party, and 3rd Party Audiences
The way user data is collected to create advertising audiences, how these data are stored, and who is responsible for these data leads to this classification of audiences:
First-Party Data
These are the data you collect directly from your audience or customers. They can come from your website, apps, CRM, surveys, purchases, newsletter subscriptions, etc. These data are extremely valuable because they are unique to your business, highly relevant, and you have complete control over them. For example, if someone buys a product on your website, that information is first-party data.
- Advantages: These are data collected directly from the company’s audience, ensuring relevance and high quality. There is complete control over these data, which are more accurate and secure from a privacy standpoint.
- Problems and Limitations: Collecting these data can be slow and costly. Additionally, the scope may be limited to the existing customer base, restricting the ability to attract new customers without expansion strategies.
Second-Party Data
Second-party data are essentially another organization’s first-party data that you choose to acquire or exchange. Usually, this is done between trusted parties that agree to share their data. While these data can be very valuable and relevant, it’s crucial to have clear agreements on how these data can be used to respect privacy and user expectations. An example might be a clothing company partnering with a sports footwear company to cross-promote products to their respective audiences.
- Advantages: These data come from a trusted source and are considered high-quality because they are essentially first-party data from another organization. They provide access to new audiences while maintaining high relevance.
- Problems and Limitations: There may be contractual limitations on how the data can be used. Also, the relevance and quality of the data depend on the original source, and there may be compatibility or privacy concerns when sharing data between companies.
Third-Party Data
These data are collected by entities that do not have a direct relationship with the user from whom the data is collected. These entities collect, aggregate, and sell these data to advertisers to expand their audiences beyond what they can achieve with just first- and second-party data. Third-party data can include demographic information, interests, online behavior, and much more, from a variety of sources. However, with increasing concerns about user privacy and changes in legislation, the use of third-party data is becoming more restricted.
- Advantages: They offer broad reach, allowing companies to target new potential customers outside their existing database. They are useful for market expansion and broad segmentation.
- Problems and Limitations:
- Dependence on Third Parties: Companies depend on third parties for the quality and accuracy of the data.
- Privacy Concerns: The use of third-party data is facing increasing regulatory restrictions, especially in Europe with the GDPR and other regions implementing similar regulations, such as CCPA in California.
- Accuracy and Relevance: The data may be less accurate or relevant than first- or second-party data since they are not collected directly from interaction with the brand.
- Decreasing Availability: With increasing privacy concerns and technological changes, such as third-party cookie blocking by popular browsers, access to third-party data is decreasing.
Each type of data has its own value and use in digital marketing strategy, and the choice between them depends on your specific goals, budget, and privacy concerns.
Third-Party Data and Privacy Regulations
About Browsing Cookies
Cookies collect user data by storing information about navigation and interactions on websites. When a user visits a website, it may send one or more cookies to the user’s browser, which stores them. These cookies can store data such as site preferences, login information, and browsing behavior. This information can then be used by the website to personalize the user experience or by advertisers to target ads based on browsing behavior.
- First-party cookies are created and used by the website the user is directly visiting. They store information such as user preferences, session data, and browsing behavior to improve the experience on that specific site.
- Second-party cookies, although less common in terminology, generally refers to first-party cookies shared or sold to another company (the ‘second party’), used for purposes such as data analysis or targeted advertising.
- Third-party cookies are created and placed by domains other than the one the user is directly visiting, often through scripts or ads embedded on the webpage.
Cookies are used to track user navigation across different websites, allowing advertisers to create detailed profiles of behavior and preferences to target personalized advertising. These cookies are fundamental to online behavioral advertising but have also raised privacy concerns and are being limited by new regulations and browser technologies.
European Cookie Regulation (Updated 2024)
The cookie law in Europe, under the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the ePrivacy Directive, requires websites to obtain explicit user consent before using cookies (except those strictly necessary for the functioning of the site). Websites must provide clear and comprehensive information about the use of cookies, including what data is collected and for what purpose. They must also offer users the option to accept or reject non-essential cookies and facilitate the withdrawal of consent at any time.
The January 2024 update additionally requires the cookie banner to include a button with the words “reject cookies,” “reject,” or similar, ensuring that the acceptance and rejection mechanisms are on equal terms.
The cookie law particularly affects third-party audiences by limiting the collection and use of data without explicit user consent. This means that advertisers and platforms must be more transparent about how they collect and use data and must offer users a clear and simple way to give or withdraw their consent. This can result in a decrease in the amount of third-party data available, impacting targeting and personalization strategies for advertising campaigns.
California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA)
The California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) is a regulation that came into effect on January 1, 2020, to increase privacy and data protection rights for California residents. Under the CCPA, consumers have fundamental rights, such as the right to know what personal data is being collected about them, the right to request the deletion of their data, the right to opt-out of the sale of their data, and the right not to be discriminated against for exercising their privacy rights.
Businesses affected by this law must comply with several obligations, including transparency in their privacy policies, providing means for consumers to make data requests, and verifying the identity of requesters to protect privacy. Additionally, companies that sell personal data must provide a visible link allowing consumers to opt-out of the sale of their personal information.
The CCPA applies to any business, regardless of location, that has annual revenues over $25 million, handles personal information of more than 50,000 California residents, or derives more than 50% of its annual revenues from selling personal information of California residents. This law has set an important precedent in US privacy legislation, influencing other states to consider similar laws.
Consent Mode: Google’s Response to Privacy Laws
Google introduced Consent Mode to help website owners comply with data privacy laws such as GDPR in Europe and CCPA in California.
Google’s Consent Mode is a tool that allows the adjustment of the use of third-party cookies, enabling or disabling Google’s cookies based on the explicit consent of the site visitors.
This mode facilitates compliance with regulations without sacrificing valuable insights from analytics and advertising, maintaining the ability to measure conversions and perform traffic analysis in an aggregated manner while respecting the privacy of users who do not wish to be tracked.
Consent Mode on Facebook and Other Social Networks
Facebook and other social networks collect user data primarily through direct interaction within their platforms. When users create accounts, share personal information, post content, interact with posts, and use various features, social networks capture this information. This collection includes demographic data, interests, platform behavior, and connections with other users. These data enable social networks to form detailed audiences for targeted advertising, offering advertisers the ability to reach specific groups based on their characteristics and behaviors.
User consent on Facebook for handling their personal data is obtained through the acceptance of the terms of service and privacy policy when creating an account. The platform also provides privacy settings and tools that allow users to manage how their data is shared and used, including options to control targeted advertising and how their information is collected through activity on other sites and apps that use Facebook services.
Consent Mode and Traditional Media
Google’s Consent Mode and similar technologies are specifically designed for the digital environment, where user tracking and data collection are primarily done through cookies and other online tracking technologies. These tools allow websites to adjust cookie usage and tracking based on user consent, which is crucial for complying with data privacy laws such as GDPR in Europe and CCPA in California.
Traditional media advertising, such as television, radio, print, and billboards, operates under a different model that does not rely on individualized tracking of user behavior through digital technologies. Here are some reasons why Consent Mode does not affect advertising in traditional media:
- No Direct Digital Tracking: Traditional media do not collect user data in the same way digital media do. For example, when you watch an ad on TV or hear one on the radio, there is no direct mechanism to track that you, specifically, have seen or heard the ad.
- Audiences Based on General Estimates: Targeting in traditional media is based on audience estimates and general demographic data, rather than on browsing behavior or individual purchase history. These estimates come from surveys and audience studies rather than digital tracking.
- Regulations Focused on Digital: Data privacy laws like GDPR and CCPA are primarily focused on the collection and use of personal data in digital environments. While these regulations also impact how personal data collected through traditional means is handled, the focus is much more relevant to online tracking and digital advertising.
- Implicit vs. Explicit Consent: In many cases, interaction with traditional media implies a level of implicit consent, where users understand that consuming free content (such as broadcast TV or radio) comes with the expectation of being exposed to advertising. In the digital environment, however, consent for tracking and data collection must be explicit and clear, according to current privacy regulations.
In summary, Google’s Consent Mode does not affect advertising in traditional media due to the fundamentally different nature in which these media operate concerning the collection and use of personal data. While digital advertising requires explicit consent for detailed tracking and ad personalization, traditional media advertising relies on more general segmentation and ad delivery methods.
Other Audiences Unaffected by Consent Mode
Google’s Consent Mode primarily affects how websites collect and use user data for advertising and analysis in the digital environment, adjusting to user consent regarding the use of cookies and similar tracking technologies. However, certain third-party audiences may be less affected or not directly affected by the implementation of Consent Mode, especially those that rely on data collection methods that do not exclusively depend on online tracking or cookies. These audiences include:
- Aggregated or Anonymized Data Audiences: Audiences formed from aggregated or anonymized data, where specific individuals are not identified, may be less susceptible to the restrictions imposed by Consent Mode. This is because the information is not directly linked to identifiable personal data collected through cookies.
- Offline Sources: Audiences built from offline data collection, such as data obtained through physical surveys, paper forms, or in-person events, are not affected by Consent Mode. These data can be digitized and used for audience segmentation without relying on online tracking.
- Contextual and Content-Based Audiences: Audiences determined by the context or content of the website, where ads are shown based on the topic of the page rather than user behavior, may not be directly affected by Consent Mode. This form of advertising relies less on individual tracking and more on the environment in which the ad is placed.
- Second-Party Data Audiences with Consent: Audiences formed from second-party data, which are obtained through agreements between companies with explicit consent to share such information, may not be affected in the same way as data collected directly through third-party cookies.
- Proprietary Platform Audiences: Platforms with large user bases that collect data through direct interactions with their services (such as social networks or search engines) can build audiences based on user behavior within their ecosystems. While Consent Mode may influence how data are collected and used, these platforms have their methods for obtaining consent and managing privacy preferences.
It’s important to note that although certain third-party audiences may not be directly affected by Consent Mode, the general trend towards greater privacy and consent in the digital realm is driving all parts of the advertising industry to reconsider how they collect and use data. This means that even audiences not currently affected may experience changes in the future as user expectations and regulations evolve.
Reorienting Your Business Strategy to Survive the Implementation of Consent Mode
Google’s Consent Mode and similar privacy regulations are changing how advertisers use third-party data, pushing the industry towards more sustainable practices focused on user privacy. This includes a greater reliance on first- and second-party data and the search for innovative approaches to targeting and personalization.
The implementation of Consent Mode can affect your business in several ways:
- Reduction of Available Data: Since Consent Mode allows users to reject the use of tracking cookies, advertisers may find a decrease in the amount of third-party data available. This is because fewer users may be contributing to the aggregated datasets sold by third-party data providers.
- Quality and Accuracy: The quality and accuracy of third-party data could be affected. With less data available due to user consent preferences, profiles generated from these data may not be as detailed and accurate as before, impacting the effectiveness of segmentation and targeting based on these data.
- Increase in the Value of 1st and 2nd Party Data: With restrictions on the use and collection of third-party data, first- and second-party data becomes even more valuable. Brands can focus more on strengthening their data collection strategies directly from their audiences and through partnerships with other companies, respectively.
- Innovation in Targeting Strategies: Advertisers may need to seek alternative and more innovative methods to segment their audiences, such as using machine learning to identify patterns in first-party data or exploring new forms of collaborations for the exchange of second-party data, always respecting user privacy.
- Emphasis on Consent and Transparency: The implementation of Consent Mode underscores the importance of user consent and transparency in data collection and use. This could lead to greater user trust, but it would also require advertisers to be clearer about how and why they collect and use data.
Emphasizing Consent and Transparency
Implementing Google’s Consent Mode on your website will help you navigate the complex online privacy environment, ensuring legal compliance, respecting user privacy, and maintaining the effectiveness of your analytics and digital advertising campaigns.
- Legal Compliance: To comply with privacy regulations that require explicit consent to collect and use users’ personal data, Consent Mode helps you manage this consent efficiently.
- Respect for User Privacy: By adjusting the use of cookies and web signals according to user consent, you demonstrate a commitment to respecting your visitors’ privacy, which can enhance trust and brand perception.
- Adaptive Analytics and Advertising: Consent Mode allows Google tools like Analytics and Ads to adapt to the user’s consent status, meaning you can still obtain valuable data and track conversions in an aggregated and anonymous manner even when users do not consent to the use of advertising or analytics cookies.
- Optimization of Advertising Campaigns: It helps optimize the performance of your advertising campaigns by adjusting data collection and conversion tracking based on user consent, allowing you to make more informed decisions about your marketing efforts.
- Adaptability and Future-Proofing: With the rapidly changing online privacy landscape and browsers increasingly restricting the use of third-party cookies, implementing solutions like Consent Mode better prepares you to adapt to these trends and ensure the continuity of your analytics and advertising campaigns in the future.
- Improvement of User Experience: By requesting and respecting user consent for tracking, you can enhance the overall user experience on your website, which is crucial for maintaining and growing your user and customer base.
Diversifying Your Advertising Strategy
Diversifying your advertising strategy in response to Consent Mode is essential to reduce dependency on Google’s cookies, adapt to privacy regulations, and maintain marketing effectiveness in a changing digital environment.
There are numerous alternative advertising platforms to Google Ads that are universally recognized for their effectiveness in reaching valuable and engaged audiences.
- Microsoft Ads: Ideal for paid search and display ads, offering a broad audience and powerful targeting capabilities.
- Facebook and Instagram: Excellent for brands seeking a visual approach and wanting to leverage detailed demographic and interest-based targeting.
- LinkedIn: The best option for B2B advertising, allowing targeting by industry, job title, and company size.
- Twitter, Snapchat, and TikTok: Can be effective depending on whether your target audience uses these platforms and how they align with your campaign goals.
- Programmatic Advertising Platforms: Allow automated buying of ad spaces across various websites, ideal for wide-reaching campaigns with specific targeting.
Choosing the right platforms requires a mix of research, experimentation, and continuous adjustments. It also takes a good specialist to do all this smoothly, so consider using skill, knowledge, and behavioral assessments and hire a professional to do this. Deeply understanding your audience and monitoring your campaign performance will help you maximize the impact of your digital advertising efforts.
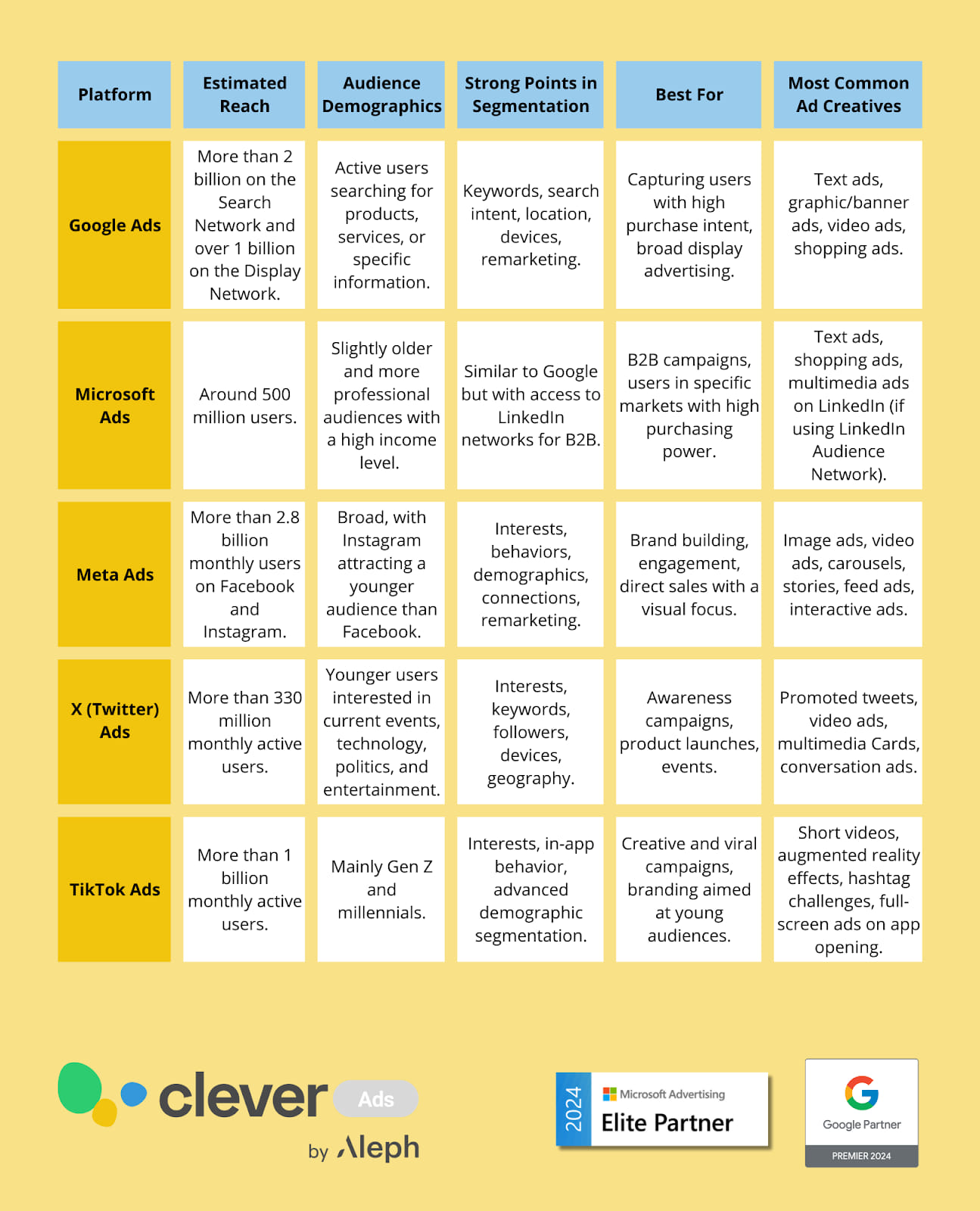
Below is a comparative table of the audiences on various advertising platforms, which can help you better understand which platform you might want to focus your advertising efforts on according to your target audience:
How to Create Campaigns and Monitor Your Multiplatform Strategy with Clever Ads
At Clever Ads, we facilitate the creation, management, and optimization of advertising campaigns across various platforms, including Google Ads, Microsoft Ads, Facebook, Instagram, TikTok, and Twitter. We use artificial intelligence to automate ad creation and optimize their performance.
Steps to Create and Monitor Campaigns
- Initial Setup: Sign up for Clever Ads and link your advertising accounts.
- Campaign Creation: Use AI tools to automatically generate optimized ads on your preferred platforms.
- Continuous Optimization: Receive personalized recommendations to improve your campaigns based on continuous data analysis.
- Multiplatform Monitoring: Use Clever Ads’ centralized dashboard to track the performance of all your campaigns from one place.
- Reports and Adjustments: Generate detailed reports and make real-time adjustments to maximize the effectiveness of your advertising strategies.
Key Benefits
- Automation: Simplifies the creation and management of ads.
- Comprehensive Analysis: Monitor and analyze performance from a single dashboard.
- Optimization: Data-driven recommendations to improve campaigns.
Enhancing Second-Party Data
Compensating for the reduction of third-party audience data with an increase in second-party audience data (second-party data) requires a focus on collaboration and data sharing with other organizations transparently and consensually. Here are several strategies you can employ to increase the volume and quality of your second-party data:
- Establish Strategic Partnerships: Seek partnerships with companies that have complementary audiences to yours but are not direct competitors. These partnerships can be based on sharing relevant data that benefits both parties, allowing access to new audience segments.
- Participate in Data Consortia: Consider joining data consortia where multiple companies share and access data securely and consensually. This can significantly expand your audience data reach and provide deeper consumer insights.
- Data Exchange Agreements: Negotiate specific data exchange agreements with related companies, ensuring that both parties benefit from the exchange. These agreements must be transparent and comply with data protection laws, ensuring user consent.
- Use Data Management Platforms (DMPs): Data Management Platforms (DMPs) can facilitate the exchange and segmentation of second-party data, allowing efficient management and enrichment of your audience profiles.
- Sponsorships and Joint Events: Organizing or sponsoring events with other companies can be an effective way to collect second-party data. Registrations for events, webinars, or online seminars offer an opportunity to gather direct information from participants interested in related topics.
- Affiliate Programs: Develop affiliate programs with other companies to promote your products or services through their channels. This not only increases your sales but also provides valuable data about referred customers.
- Content Exchange: Collaborate with other companies to exchange relevant content that can attract their respective audiences. This can include blog posts, case studies, research reports, etc., which can be promoted through each company’s channels, collecting data from interested users.
- Privacy and Consent: It is crucial that any data exchange or collaboration in handling second-party data is carried out with full transparency and in compliance with data protection laws. Ensure that consent to share data is obtained clearly and that users have control over their data.
By implementing these strategies, you can compensate for the loss of third-party data by building stronger, more strategic relationships with other companies, allowing you to access a richer and more diversified audience database that can effectively drive your marketing and advertising efforts.
Enriching First-Party Data
Compensating for the reduction in third-party audience data due to stricter privacy regulations and technological changes, such as the gradual elimination of third-party cookies, involves focusing on increasing and enriching your first-party data base.
Here’s how to do it through various actions and strategies:
- Improve User Experience to Encourage Direct Interaction: Optimize your website and apps to make them more attractive and easy to use, encouraging users to interact more with your brand and share their data voluntarily.
- Offer Value in Exchange for Data Consent: Create valuable incentives for your users in exchange for their information and consent. This can include access to exclusive content, discounts, promotions, high-quality newsletter subscriptions, or early access to new products or services.
- Implement Loyalty and Rewards Programs: Develop loyalty programs that reward customers for sharing personal information and their loyalty to the brand. These rewards can include points, discounts, gifts, or exclusive benefits.
- Use Surveys and Feedback to Collect Data: Actively conduct surveys and request feedback from your customers. This not only provides valuable data but also involves customers in the development of your products or services.
- Organize Virtual and In-Person Events: Events, whether webinars, workshops, or in-person meetings, are excellent opportunities to collect first-party data. Ensure to promote pre-registration and use the opportunity to gather relevant information from participants.
- Create High-Quality Content that Requires Registration: Develop premium content such as research reports, guides, tutorials, or courses that are available only through registration. This can encourage users to share their contact information in exchange for valuable content.
- Optimize Registration and Subscription Forms: Ensure that registration or subscription forms are simple, straightforward, and non-invasive. Ask for only essential information to reduce friction and increase conversion rates.
- Promote User Account Creation: Encourage visitors to your website to create an account for a personalized experience. This not only improves the user experience but also provides valuable data.
- Implement Retargeting and Remarketing Campaigns: Although they technically use first-party data, these campaigns can be enriched with insights to improve personalization and effectiveness, collecting more data in the process.
- Be Transparent About Data Use: Clearly communicate how personal data will be used to improve the user experience, ensuring informed consent and building trust in your brand.
Focusing on these strategies to increase your first-party audiences will not only compensate for the loss of access to third-party data but also build a richer and more engaged database, allowing you to personalize and improve your marketing efforts more effectively and sustainably.
There are some challenges and considerations you should take into account when reinforcing and maximizing your first-party data.
- Need for Consent Management Tools and Strategies: To effectively collect and use first-party data under Consent Mode, companies need to implement technological solutions that manage user consent efficiently and comply with privacy regulations. This can be challenging, especially for small and medium-sized businesses with limited resources.
- Impact on Measurement and Analysis: Although first-party data are collected directly, Consent Mode still affects how site interactions and conversions are measured if users choose not to consent to analytical or advertising cookies. This can make it harder for advertisers to measure campaign performance and site effectiveness without proper adaptation to these restrictions.
- Innovation in Data Capture: Companies may need to be more creative in how they capture and use first-party data, ensuring they offer value in exchange for user consent, such as exclusive content, discounts, or personalized experiences.
Advantages of Implementing Consent Mode
Google’s Consent Mode promotes a more privacy-focused approach and first-party data, which can be beneficial for both users and brands seeking to build stronger, trust-based relationships with their customers. Implementing this tool on your website offers several key advantages, especially in terms of regulatory compliance, data optimization, and user experience.
- Privacy Regulation Compliance: Consent Mode helps ensure that your website complies with privacy laws such as GDPR in Europe and CCPA in California. By adjusting cookie use and tracking based on user consent, your site can operate legally in regulated markets, avoiding potential fines and litigation.
- Preservation of Analytical Data: One of the main advantages of Consent Mode is that it allows websites to continue collecting important analytical data, although limited, even when users do not consent to non-essential cookies. This is achieved through the aggregation and anonymization of data, ensuring you can still gain valuable insights into traffic and user behavior without compromising privacy.
- Advertising Optimization: Consent Mode also adjusts how advertising cookies are handled. If a user rejects advertising cookies, Google can use modeled conversion signals to help measure the impact of ad campaigns without using third-party cookies. This means you can continue optimizing your advertising campaigns based on actual performance, even though individualized tracking is limited.
- Enhance User Experience: By implementing Consent Mode, you provide users with greater control over their personal data, which can improve their perception and trust in your brand. Users are more likely to interact with sites that respect their privacy and offer clear options regarding data use.
- Adaptability to Future Privacy Changes: With the constantly evolving online privacy landscape, Consent Mode prepares you for future changes in laws and technologies. By already having a system that handles consent flexibly, your site will be better equipped to adapt to new regulations or user expectations.
- Maintenance of Advertising Relevance: Even if users choose not to allow advertising cookies, Consent Mode allows Google to apply techniques such as modeled conversion to estimate ad performance. This helps maintain the relevance and effectiveness of your advertising efforts, crucial for ROI in digital marketing.
In summary, implementing Consent Mode is a strategic decision that protects both your users and your business, ensuring regulatory compliance, respecting user privacy, and maintaining the effectiveness of your digital advertising campaigns.




